14 File System Implementation
Contents
- File-System Structure
- File-System Implementation
- Directory Implementation
- Allocation Methods
- Free-Space Management
- Efficiency and Performance
- Recovery
- NFS
- Example: WAFL File System
Objectives
To describe the details of implementing local file systems and directory structures
To describe the implementation of remote file systems
To discuss block allocation and free-block algorithms and trade-
offs
File-System Structure
- File structure
- Logical storage unit 逻辑存储单元
- Collection of related information 相关信息的收集
- File system resides on secondary storage (disks)
- Provided user interface to storage, mapping logical to physical 提供存储用户界面,将逻辑映射到物理
- Provides efficient and convenient access to disk by allowing data to be stored, located retrieved easily 通过允许存储数据、轻松检索来提供对磁盘的高效便捷访问
- Disk provides in-place rewrite and random access 磁盘提供就地重写和随机访问
I/O transfers performed in blocks of sectors (usually 512 bytes)
- File control block – storage structure consisting of information about a file
- Device driver controls the physical device 设备驱动程序控制物理设备
- File system organized into layers 文件系统组织成层
File System Layers (Cont.)
Each with its own format (CD-ROM is ISO 9660; Unix has UFS, FFS; Windows has FAT, FAT32, NTFS as well as floppy, CD, DVD Blu-ray, Linux has more than 40 types, with extended file system ext2 and ext3 leading; plus distributed file systems, etc.)
File-System Implementation
We have system calls at the API level, but how do we implement their functions? 我们在 API 级别有系统调用,但我们如何实现它们的功能?
On-disk and in-memory structures
Boot control block contains info needed by system to boot OS from that volume 启动控制块包含系统从该卷启动操作系统所需的信息
Needed if volume contains OS, usually first block of volume
Volume control block (superblock, master file table) contains volume details 卷宗控制块 (超级块,主文件表)包含卷详细信息
Total # of blocks, # of free blocks, block size, free block pointers or array
Directory structure organizes the files 目录结构组织文件
Names and inode numbers, master file table
Directory Implementation
Allocation Methods
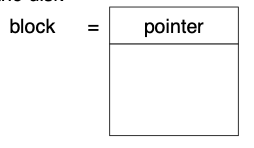
Allocation Methods - Linked
Linked allocation – each file a linked list of blocks 链接分配 - 每个文件一个链接的块列表
- File ends at nil pointer 文件在零指针处结束
- No external fragmentation 没有外部碎片
- Each block contains pointer to next block
- No compaction, external fragmentation 无压实,外部碎片
- Free space management system called when new block needed 当需要新块时调用自由空间管理系统
- Improve efficiency by clustering blocks into groups but increases internal fragmentation 通过将块聚类为组来提高效率,但会增加内部碎片
- Reliability can be a problem 可靠性可能是一个问题
- Locating a block can take many I/Os and disk seeks 定位块可能需要许多 I/O 和磁盘查找
FAT Variation
FAT (File Allocation Table 文件分配表) variation
- Beginning of volume has table, indexed by block number
- Much like a linked list, but faster on disk and cacheable
- New block allocation simple
Each file is a linked list of disk blocks: blocks may be scattered anywhere on the disk